The Houthis, also called Ansar Allah (or “supporters of God”), are a violent militia group that at the moment train de facto management over a lot of northern Yemen. Shaped within the Nineties, the group was named after its founder, Hussein Badreddin al-Houthi, they usually comply with the Zaidi department of Shia Islam which represents 20-30% of Yemen’s inhabitants.
The group’s management has been drawn from the Houthi tribe, which is a part of one of many three main tribal confederations in Yemen: the Hashid, the Madhaj and the Bakil. The Houthis are a part of the Bakil confederation, the most important tribal group in Yemen. Because the UK and US launch army strikes on the Yemeni group, after a spate of assaults by the Iran-backed militia on Pink Sea transport, right here’s 4 issues that it is advisable to learn about them.
1. Why did the Houthis type?
As a way to perceive the rise of the Houthis, it’s first vital to put out the turbulent historical past of Yemen. Yemen has struggled to construct a unified and efficient state and has been stricken by weak establishments, weak nationalism, insurgency and secessionism since its formation in 1990. The world that contains Yemen at present was cut up into two territories, north and south from the nineteenth century to 1990. After the collapse of the Ottoman empire, North Yemen grew to become unbiased in 1918. The south of Yemen was beneath British management till 1967. The Individuals’s Democratic Republic of Yemen (South Yemen) was unbiased from 1967 to 1990. The 2 had been unified in 1990.
Tribal identities stay robust, notably within the north, and many various teams have held energy. The Zaydi Shiites have fought for management of the territory that we now know as Yemen for hundreds of years, with some success, and beneath the Houthis, management elements of northern Yemen.
If we quick ahead to the fashionable period, Yemen has confronted fixed battle and state failure. The north was dominated by former Yemeni president Ali Abdullah Saleh (a dictator who’s a part of one other tribal group), since 1978, who then took over as president of a newly unified Yemen in 1990 . Saleh’s kin managed core elements of the military and financial system – and corruption was rife.
Tensions arose over the overwhelming majority of Yemen’s sources flowing to Sana’a, the capital of north Yemen, and specifically to Saleh’s Sanhan clan, which is part of the Hashid federation. Although the central authorities managed to maintain the nation collectively (Saleh notably claimed that ruling Yemen was like “dancing over the heads of snakes”) after the south tried to secede in 1994, there have been many teams that held grievances towards the Saleh-led authorities.
Probably the most notable group to problem the central authorities in Yemen had been the Houthis. Along with enduring a long time of political marginalisation, neglect, financial exclusion and generally terror by the central authorities, the Houthis had been involved by rising Saudi affect within the nation — and with the rising energy of Salafism and Wahhabism (seen as imported Saudi non secular doctrines) specifically.
However the tipping level for the Houthi motion was possible the US invasion of Iraq in 2003. Influenced by the success of Lebanon-based militants Hezbollah in repelling western forces, the Houthis drew inspiration and gained assist from the Lebanese-based group, in addition to Iran — although their officers deny their connection.
2. How did the Houthis achieve energy?
To deal with the rising energy of the Houthis, Saleh launched a army marketing campaign in 2003, with the assistance of Saudi Arabia. Although Saleh’s forces managed to kill Houthi chief, Hussein al-Houthi in 2004, the Houthis usually bested Saleh and the Saudi military regardless of billions of {dollars} spent by the latter.
Certainly, the Houthis proved to be a formidable drive for the Saudis to contest with, daring to cross into Saudi Arabia in 2009, and forcing the dominion to deploy its military to handle the rising Houthi menace.
For the reason that Yemeni revolution erupted in 2011, the Houthis fought to oust Saleh from energy, solely to later be a part of forces with Saleh in 2015. When their alliance crumbled, it was the Houthis who had the higher hand, with the insurgent group killing Saleh in December 2017.
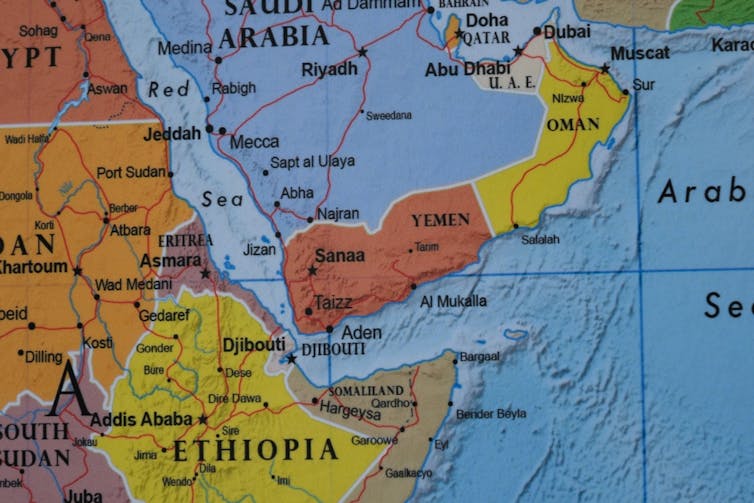
The Houthis have additionally been a serious drive within the ongoing Yemeni civil struggle (which started in 2014), which has prompted an estimated 377,000 deaths, lots of them civilians. Although it’s the authorities within the south that’s internationally recognised, the Houthis have taken over a lot of northern Yemen, since they stormed Sana’a in 2014. They management the important thing port of Hudeidah, which generates as much as US$1 billion (£784,000,000) in revenues for the Houthi authorities.
Matthew Nichols1/Shutterstock
3. What’s their regional affect?
At the moment, the Houthis have an estimated 20,000 fighters. For the reason that dying of al-Houthi, the motion has been primarily led by his brother, Abdul-Malik al-Houthi, who has said that he is not going to hesitate to assault the US and its allies.
For the reason that struggle began in Gaza in October, the Houthis have tried to capitalise on the battle to lift their worldwide profile, and as a present of energy that would achieve them extra negotiating affect. Claiming to be in solidarity with the Palestinian folks, the Houthis initiated a collection of assaults on industrial ships within the Pink Sea, the slender finish of which is neglected by Yemen. Probably the most brazen assault came about on November 19 2023, when militants used a helicopter to abduct the crew of a automotive service that was linked to an Israeli businessman.
4. Do they management Pink Sea entry?
Although a lot of the Houthi assaults on the Pink Sea haven’t been profitable, they’ve compelled hundreds of ships to bypass the route and divert round South Africa—including vital prices and time.
In retaliation for the handfuls of assaults on the Pink Sea, the US and the UK have responded with their largest assault towards the Houthis since 2016 , when the US struck three Houthi missile websites with cruise missiles after the Houthis fired on the US navy and industrial vessels. This referred to as a brief halt to Houthi assaults. However now, with the Houthis assured that they’ve been victorious towards the Saudis and the west in Yemen, the rebels appear extra keen than ever to tackle the US head on.




